The RF JSON2RC module performs post-processing of JSON files generated by DRACO, into RC files. These can be further processed via the rf-norm module to obtain normalized reactivity profiles for structure prediction with the rf-fold module.
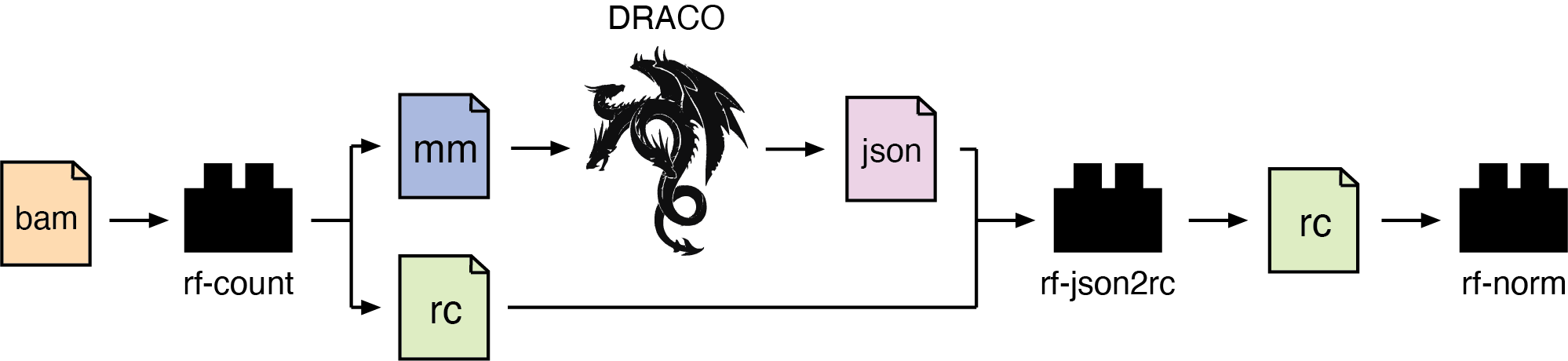
Usage
To list the required parameters, simply type:
$ rf-json2rc -h
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -o or --output-dir | string | Output directory for writing counts in RC (RNA Count) format (Default: rf_json2rc/) |
| -ow or --overwrite | Overwrites the output directory if already exists | |
| -j or --json | string | A comma-separated list of DRACO JSON files from replicate experiments |
| -r or --rc | string | A comma-separated list of RC files from replicate experiments Note: the RC files must follow the same order of the JSON files |
| -rci or --rc-index | string | A comma-separated list of RCI index files Note #1: the RCI indexes must follow the same order of the RC files. Note #2: if a single RCI index is provided, it will be used for all the RC files. |
| -ep or --median-pre-cov | int | Windows with median preCoverage (see DRACO docs for more information) below this threshold, will be discarded (Default: 1000) |
| -ec or --median-cov | int | Windows with a mediam cumulative coverage (the sum of the coverage across all the conformations for that window) below this threshold, will be discarded (Default: 5000) |
| -sz or --skip-zero-cluster-wins | Skips windows for which DRACO failed to identify the number of conformations | |
| -nc or --min-confs | int | Windows forming less than this number of conformations will be discarded (Default: 2) |
| -xc or --max-confs | int | Windows forming more than this number of conformations will be discarded (Default: no limit) |
| -nm or --no-merge-overlapping | Disables merging of intra-replicate concordant overlapping windows | |
| -mom or --min-overlap-merge | float | Minimum fractional overlap between two concordant overlapping windows to be merged (0-1, Default: 0.5) |
| -mcm or --min-corr-merge | float | Minimum average correlation between corresponding conformations for concordant overlapping windows to be merged (0-1, Default: 0.7) |
| -e or --extend | int | Windows are extended by these many bases upstream and downstream (Default: off) Note: these bases will be assigned a coverage and mutation count of 0 |
| -sr or --surround-to-rc | Instead of getting coverage and mutation count of 0, bases in up/downstream extensions will be assigned the same coverage and mutation count they have in the input RC files (requires -e) |
|
| -i or --ignore-terminal | float | Coverage and mutation counts for this fraction of bases at window termini will be set to 0 (0-0.2, Default: 0.05) |
| -ki or --keep-ignored | Bases ignored during correlation calculation, will be kept in the output RC files Note: by default, both counts and coverage for these bases is set to 0 |
|
| -mor or --min-overlap-reps | float | Minimum fractional overlap between windows across replicates to be merged (0-1, Default: 0.75) |
| -mcr or --min-corr-reps | float | Minimum correlation between corresponding conformations for matched windows across replicates, to be reported (0-1, Default: 0.7) |
| -s or --spearman | Spearman will be used instead of Pearson for correlation analysis | |
| -cf or --cap-mut-freqs | float | Mutation frequencies will be capped to this value for correlation calculation (>0-1, Default: 1 (no cap)) |
Understanding the algorithm
Windows are pre-filtered based on a number of criteria:
- The median preCoverage (the coverage calculated only on the reads used for the spectral analysis) must be ≥
--median-pre-cov - The median cumulative coverage (the sum of the coverage across all the conformations for a given window) must be ≥
--median-cov - If
--skip-zero-cluster-winshas been specified, windows for which DRACO failed to identify the number of conformations will be discarded, otherwise they will be assumed to form a single conformation - Windows forming <
--min-confsconformations will be discarded - Windows forming >
--max-confsconformations will be discarded
DRACO analysis is performed in sliding windows. When two consecutive windows are found to form the same number of conformations, they are automatically merged. However, in certain cases, it might be possible for two non-consecutive overlapping windows forming the same number of conformations, to be interspersed among windows forming a different number of conformations.
Let's consider the following example:

In this case, four windows overlap. Of these, three form 2 conformations, while one forms 3 conformations. As long as the --no-merge-overlapping parameter has not been specified, the first step of the analysis will consist of merging overlapping windows forming a concordant number of conformations. The minimum overlap between two windows must be ≥ --min-overlap-merge × the length of the smaller window. In the above example, Win #3 overlaps by 70% of its length with Win #1. Similarly, 90% of Win #4 overlaps with Win #3, therefore all three windows could in principle be merged (with default parameters).
Before being merged, however, the overlapping segments of the conformations making up the two overlapping windows need to be matched.

To this end, the pairwise correlation between the reactivity profile for each conformation of the two windows is calculated at the level of the overlap. Any possible combination is evaluated, and the one yielding the highest average correlation coefficient is selected. If the average correlation coefficient exceeds the --min-corr-merge threshold, the two windows (and corresponding conformations) are merged. If the average correlation does not exceed the threshold, the two windows are not merged. Pearson correlation is used by default; alternatively, Spearman correlation can be used, by specifying the --spearman parameter. The stoichiometries of the different conformations for the merged windows are averaged.
If a single JSON file has been provided, the resulting windows are then directly reported in the RC file. If multiple JSON files have been provided, instead, the algorithm will first look for windows common to all replicates.

Windows overlapping across all the replicates, coherently forming the same number of conformations, are merged if the minimum overlap is ≥ --min-overlap-reps × the length of the smaller window. Only windows common to all replicates will be reported. In the above example Win #1 and Win #2 from Replicate #1 overlap with their counterpart from Replicate #2, while Win #3 does not; therefore, only Win #1 and Win 2 could in principle be reported. Analogously to what happens when merging overlapping windows within the same replicate, also in this case the pairwise correlation between the reactivity profile for each conformation of the windows is calculated, and the one yielding the highest average correlation coefficient is selected. If the average correlation coefficient exceeds the --min-corr-reps threshold, the windows are merged, and reported in the resulting RC file.
An RC file will be generated for each replicate being analyzed. Naming and sorting of the windows is consistent across replicates. For each window, different conformations are marked by the _c<n> suffix, where n is an arbitrary number assigned to a specific conformation. When reporting windows in the output RC file, these can be enlarged both upstream and downstream by --extend bases, to account for the possibility that the structure(s) formed by a given window might involve extra bases outside of the window's boundaries. By default, these extra bases are assigned both mutation count and coverage of 0. If --surround-to-rc has been specified, however, the mutation count and coverage for these bases will be directly extracted from the corresponding RC file provided via --rc. This file is supposed to be the RC file generated by rf-count alongside the MM file that has been analyzed with DRACO. Furthermore, to account for the lower reliability of bases closer to window boundaries, up to 20% of the terminal bases in a window can be masked by specifying the --ignore-terminal parameter; when doing so, mutation counts and coverage for these bases will be set to 0.
Alongside with the RC files, the stoichiometries.txt file will be generated, with the following structure:
Transcript Start End extStart extEnd Replicate_1 Replicate_2
Transcript_1 704 1022 654 1072 0.562;0.438 0.541;0.459
Transcript_1 1024 1358 974 1408 0.537;0.463 0.537;0.463
...
Transcript_n 27984 28294 27934 28344 0.570;0.430 0.510;0.490
Transcript_n 29184 29358 29134 29408 0.380;0.314;0.307 0.344;0.299;357
where Transcript is the transcript ID, start and end are the coordinates (0-based) of the window, and extStart and extEnd are the coordinates of the window after being extended by --extend bases. Following these columns, a column will be present for each replicate having been analyzed, reporting the relative stoichiometries of the conformations for that window.